
Details of Post Graduate Diploma in Information Technology
This job oriented course is a one year complete course for specialisation in Programming process, packaged with complete knowledge for the present Job requirements. As the requirements of the organisation keeps on changing according to technologies we make sure that the course is continuously updated to keep phase of the requirement of the industry this one year course comes with the 100% JOB Assurance guarantee.
PGDIT is a full-time one-year postgraduate course divided into two semesters. The IT industry has emerged as one of the Indian economy's fastest growing sectors. With such unprecedented growth in the IT industry, a growing number of organizations need skilled manpower in information technology, IT business aspect, technology systems, effective technology management, business strategies, and the implementation of designed database models.
PGDIT teaches application development tools for implementing, designing and documenting reusable components in the field of IT graphic and physical user interfaces, laws, standards, regulations and contractual obligations. Big Data concepts for which the volume and variety of data could involve dozens of potentially conflicting obligations and standards are also part of the syllabus of PGDIT.
The course allows candidates to perform a multiplicity of tasks related to information in all relevant business areas, deal with structuring unstructured problems and IT-based solutions to complex situations. The nature and role of management support systems, management decision-making and decision support systems, network management and network engineering techniques are also taught.
Post Graduate Diploma in Information Technology Highlights
Course Outcome-Post Graduate Diploma in Information Technology

[A] DCA
 Computer Fundamentals, Computer Typing
Computer Fundamentals, Computer Typing
 Theory on Software, Hardware, Networking & Internetworking
Theory on Software, Hardware, Networking & Internetworking  Microsoft Windows Based Desktop Operating Systems
Microsoft Windows Based Desktop Operating Systems Microsoft Office Suit (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Access)
Microsoft Office Suit (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Access)
 Microsoft Office Suit (Outlook, Picture Manager, Project)
Microsoft Office Suit (Outlook, Picture Manager, Project) Productivity Product (Adobe Acrobat)
Productivity Product (Adobe Acrobat) Connectivity (LAN, Wireless, Remote Access)
Connectivity (LAN, Wireless, Remote Access)
 Internet (Browsing, E-Mail, Chat, Search Engines, download, Upload etc.)
Internet (Browsing, E-Mail, Chat, Search Engines, download, Upload etc.) Storage & Archive Services Scanning, Printing, Multimedia
Storage & Archive Services Scanning, Printing, Multimedia
[B]. DSP
C Programming
Course outline
 Introduction to compiling and software development
Introduction to compiling and software development  Basic scalar data types and their operators
Basic scalar data types and their operators  Flow control
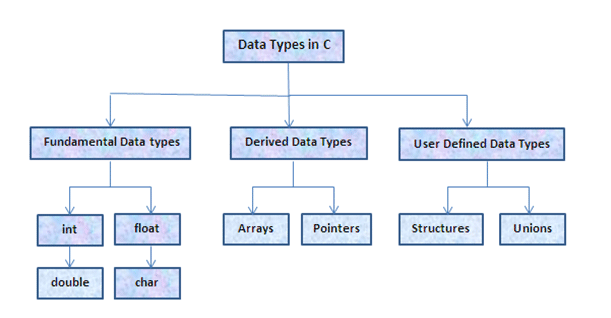
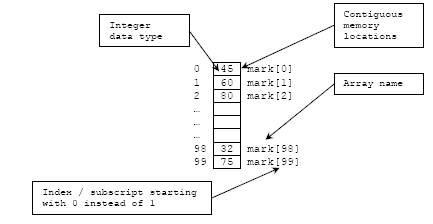
Flow control  Complex data types: arrays, structures and pointers
Complex data types: arrays, structures and pointers  Structuring the code: functions and modules
Structuring the code: functions and modules  Preprocessing source code
Preprocessing source code
Chapters
 Absolute basics
Absolute basics  Languages: natural and artificial
Languages: natural and artificial  Machine languages
Machine languages  High-level programming languages
High-level programming languages  Obtaining the machine code: compilation process
Obtaining the machine code: compilation process  Recommended readings
Recommended readings  Your first program
Your first program  Variable – why?
Variable – why?  Integer values in real life and in “C”, integer literals
Integer values in real life and in “C”, integer literals
 Floating point values in real life and in “C”, float literals
Floating point values in real life and in “C”, float literals  Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic operators  Priority and binding
Priority and binding  Post- and pre -incrementation and -decrementation
Post- and pre -incrementation and -decrementation  Operators of type op=
Operators of type op=  Char type and ASCII code, char literals
Char type and ASCII code, char literals  Equivalence of int and char data
Equivalence of int and char data  Comparison operators
Comparison operators  Conditional execution and if keyword
Conditional execution and if keyword
 printf() and scanf() functions: absolute basics
printf() and scanf() functions: absolute basics
 Flow control
Flow control
 Conditional execution continued: the “else” branch
Conditional execution continued: the “else” branch
 More integer and float types
More integer and float types
 Conversions – why?
Conversions – why?
 Typecast and its operators
Typecast and its operators
 Loops – while, do and for
Loops – while, do and for
 Controlling the loop execution – break and continue
Controlling the loop execution – break and continue
 Logical and bitwise operators
Logical and bitwise operators
 Switch: different faces of ‘if’
Switch: different faces of ‘if’  Arrays (vectors) – why do you need them?
Arrays (vectors) – why do you need them?  Sorting in real life and in a computer memory
Sorting in real life and in a computer memory  Initiators: a simple way to set an array
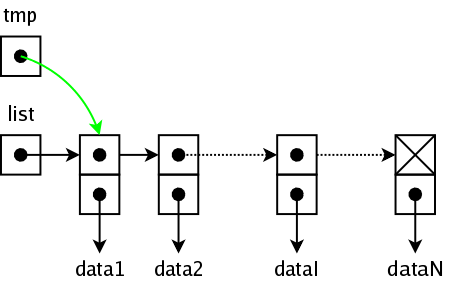
Initiators: a simple way to set an array  Pointers: another kind of data in “C”
Pointers: another kind of data in “C”  An address, a reference, a dereference and the sizeof operator
An address, a reference, a dereference and the sizeof operator  Simple pointer and pointer to nothing (NULL) & operator
Simple pointer and pointer to nothing (NULL) & operator  Pointers arithmetic
Pointers arithmetic  Pointers vs. arrays: different forms of the same phenomenon
Pointers vs. arrays: different forms of the same phenomenon  Using strings: basics
Using strings: basics  Basic functions dedicated to string manipulation
Basic functions dedicated to string manipulation
 Memory management and structures
Memory management and structures  The meaning of array indexing
The meaning of array indexing  The usage of pointers: perils and disadvantages
The usage of pointers: perils and disadvantages Void type
Void type  Arrays of arrays and multidimensional arrays
Arrays of arrays and multidimensional arrays  Memory allocation and deallocation: malloc() and free() functions
Memory allocation and deallocation: malloc() and free() functions  Arrays of pointers vs. multidimensional arrays
Arrays of pointers vs. multidimensional arrays Structures – why?
Structures – why?  Declaring, using and initializing structures
Declaring, using and initializing structures Pointers to structures and arrays of structures
Pointers to structures and arrays of structures  Basics of recursive data collections
Basics of recursive data collections
 Functions – why?
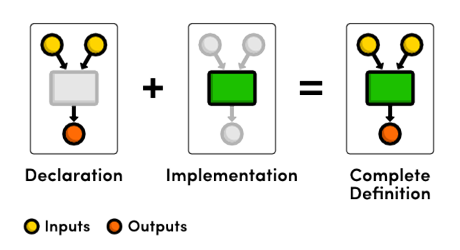
Functions – why?  How to declare, define and invoke a function
How to declare, define and invoke a function Variables' scope, local variables and function parameters
Variables' scope, local variables and function parameters  Pointers, arrays and structures as function parameters
Pointers, arrays and structures as function parameters  Function result and return statement
Function result and return statement
 Void as a parameter, pointer and result
Void as a parameter, pointer and result
 Parameterzing the main function
Parameterzing the main function
 External function and the extern declarator
External function and the extern declarator
 Header files and their role
Header files and their role
 Files vs. streams: where does the difference lie?
Files vs. streams: where does the difference lie? Header files needed for stream operations
Header files needed for stream operations
 Opening and closing a stream, open modes, errno variable
Opening and closing a stream, open modes, errno variable Reading and writing to/from a stream
Reading and writing to/from a stream  Predefined streams: stdin, stdout and stderr
Predefined streams: stdin, stdout and stderr  Stream manipulation: fgetc(), fputc(), fgets() and fputs() functions
Stream manipulation: fgetc(), fputc(), fgets() and fputs() functions  Raw input/output: fread() and fwrite() functions
Raw input/output: fread() and fwrite() functions  Preprocessor and complex declarations
Preprocessor and complex declarations  Preprocessor – why?
Preprocessor – why?  #include: how to make use of a header file
#include: how to make use of a header file
 #define: simple and parameterized macros
#define: simple and parameterized macros  #undef directive
#undef directive Predefined preprocessor symbols
Predefined preprocessor symbols Macro operators: # and ##
Macro operators: # and ##  Conditional compilation: #if and #ifdef directives
Conditional compilation: #if and #ifdef directives  Avoiding multiple compilations of the same header files
Avoiding multiple compilations of the same header files  Scopes of declarations, storage classes
Scopes of declarations, storage classes  User defined types-why?
User defined types-why?  Pointers to functions
Analyzing and creating complex declarations
Pointers to functions
Analyzing and creating complex declarations
C++ Programming Language
Description
Objective
Prerequisite
 What is C++? , Why C++?
What is C++? , Why C++?  C and C++
C and C++  Exception Handling
Exception Handling  Object Oriented Programming
Object Oriented Programming  Standard Template Library
Standard Template Library
 Types
Types  Booleans
Booleans  Integer Types
Integer Types  Floating-Point Types
Floating-Point Types Sizes
Sizes  Void
Void  Enumerations
Enumerations  Declarations
Declarations


 Pointers
Pointers  Arrays
Arrays  Pointers into Arrays
Pointers into Arrays  Constants
Constants  References
References  Pointers to void
Pointers to void  Structures
Structures
 A Deck Calculator
A Deck Calculator  Operator Summary
Operator Summary  Statement Summary
Statement Summary  Comments and Indentation
Comments and Indentation
 Function Declarations
Function Declarations  Argument Passing
Argument Passing  Value Return
Value Return  Overloaded Function Names
Overloaded Function Names  Default Arguments
Default Arguments  Pointer to Function
Pointer to Function  Macros
Macros
 Namespaces
Namespaces
 Exceptions
Exceptions
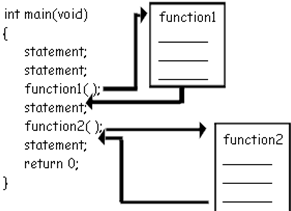
 Separate Compilation
Separate Compilation Linkage
Linkage  Using Header Files
Using Header Files  Programs
Programs
 Classes
Classes  Access Control
Access Control  Constructors
Constructors  Member functions
Member functions Static members
Static members  Destructors
Destructors Memory allocation
Memory allocation  Member initialization
Member initialization
 Introduction
Introduction  Operator Functions
Operator Functions A Complete Number Type
A Complete Number Type  Conversion Operators
Conversion Operators  Friends
Friends  Large Objects
Large Objects  Essential Operators
Essential Operators  Subscripting
Subscripting  Functions Calls
Functions Calls  Dereferencing
Dereferencing  Increment and Decrement
Increment and Decrement  A String Class
A String Class
 Introduction
Introduction
 Derived Classes
Derived Classes
 Abstract Classes
Abstract Classes
 Design of Class Hierarchies
Design of Class Hierarchies
 Class Hierarchies and Abstract Classes
Class Hierarchies and Abstract Classes
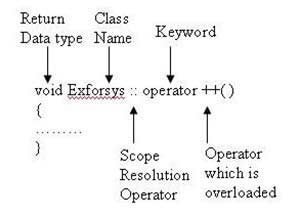
Linux Basic commands
| Linux Basic commands |
 History,features of unix, difference between Unix and Linux History,features of unix, difference between Unix and Linux |
| Unix System Architecture |
 Kernel,Shells and GUI and File system Kernel,Shells and GUI and File system |
 Application Program,Shell prompt Application Program,Shell prompt |
| Login process |
 TTY terminal,Graphical terminal, Changing password TTY terminal,Graphical terminal, Changing password |
| Unix Command Format |
 General rules for a unix command, types of commands General rules for a unix command, types of commands |
| General purpose Commands |
 echo,printf,tput,cal,date,tty,Uname,Who,Who am I,bc, pr echo,printf,tput,cal,date,tty,Uname,Who,Who am I,bc, pr |
| Unix File System |
 Unix File System Architecture,Types of files Unix File System Architecture,Types of files
|
| Directory Related Commands |
 pwd,cd,mkdir,rdir,creation of sub directory pwd,cd,mkdir,rdir,creation of sub directory |
| File Related Commands |
 cat,cp,mv,rm,touch,ls, commands to display the conents of file. cat,cp,mv,rm,touch,ls, commands to display the conents of file. |
 comparing files,file permission notation,File access permission comparing files,file permission notation,File access permission |
 chaning file permissions. chaning file permissions. |
| I/O Redirecton |
 Pipe and Pipeline,Filter(sort,cut,paste,uniq,tr,wc,cat,grep) Pipe and Pipeline,Filter(sort,cut,paste,uniq,tr,wc,cat,grep) |
| The Stream Editor(sed) |
 sed commands sed commands |
| Unix system calls |
 open,close,unlink,lseek,fork,wait open,close,unlink,lseek,fork,wait |
| Compressign and Decompressing File, Communicaton |
| Shell programming |
 Vi editor, execute shell script Vi editor, execute shell script |
 control statements, looping statements,programs on shell control statements, looping statements,programs on shell |
[C]. DAP
 Retriving data using the SQL select statement]
Retriving data using the SQL select statement]  Restricting and sorting data
Restricting and sorting data  Using single row function to customize output.
Using single row function to customize output. Reporting aggregated data using the grout function.
Reporting aggregated data using the grout function.  Displaying data from multiple tables –I
Displaying data from multiple tables –I  Displaying data from multiple tables-II
Displaying data from multiple tables-II  Using sub queries to solve problems
Using sub queries to solve problems Using set operators
Using set operators  Manipulating data
Manipulating data  Using DDL statements to create and manage tables
Using DDL statements to create and manage tables
 Creating other schema objects
Creating other schema objects
 Managing objects with data dictionary
Managing objects with data dictionary
 Controlling User access
Controlling User access
 Managing schema objects
Managing schema objects
 Manipulating large data sets
Manipulating large data sets
 Generating report by grouping related data
Generating report by grouping related data
 Managing data in different time zones
Managing data in different time zones
 Retrieving data using sub queries
Retrieving data using sub queries
 Hierarchical retrieval
Hierarchical retrieval
 Regular expression support
Regular expression support


 Introduction
Introduction  Declaring Variables
Declaring Variables  Writing Executable Statements
Writing Executable Statements  Interacting with Oracle Server
Interacting with Oracle Server  Writing Control Structures
Writing Control Structures  Working with Composite Data Types
Working with Composite Data Types  Writing Explicit Cursors
Writing Explicit Cursors  Writing Implicit Cursors
Writing Implicit Cursors  Handling Exceptions
Handling Exceptions  Creating Procedures
Creating Procedures
 Creating Functions
Creating Functions  Managing Subprograms
Managing Subprograms  Creating Packages
Creating Packages  More Package concepts
More Package concepts  Oracle supplied Packages
Oracle supplied Packages  Manipulating Large Objects
Manipulating Large Objects  Creating Database Triggers
Creating Database Triggers More Trigger concepts
More Trigger concepts  Managing Dependents
Managing Dependents
 Retriving data using the SQL select statement]
Retriving data using the SQL select statement]
 Restricting and sorting data
Restricting and sorting data
 Using single row function to customize output.
Using single row function to customize output.
 Reporting aggregated data using the grout function.
Reporting aggregated data using the grout function.
 Displaying data from multiple tables –I
Displaying data from multiple tables –I
 Displaying data from multiple tables-II
Displaying data from multiple tables-II
 Using sub queries to solve problems
Using sub queries to solve problems
 Using set operators
Using set operators
 Manipulating data
Manipulating data
 Using DDL statements to create and manage tables
Using DDL statements to create and manage tables
 Creating other schema objects
Creating other schema objects  Managing objects with data dictionary
Managing objects with data dictionary  Controlling User access
Controlling User access  Managing schema objects
Managing schema objects  Manipulating large data sets
Manipulating large data sets  Generating report by grouping related data
Generating report by grouping related data  Managing data in different time zones
Managing data in different time zones  Retrieving data using sub queries
Retrieving data using sub queries  Hierarchical retrieval
Hierarchical retrieval  Regular expression support
Regular expression support

[D]. DWD
1. Basic principles involved in developing a web site
 Planning process
Planning process  Five Golden rules of web designing
Five Golden rules of web designing  Designing navigation bar
Designing navigation bar  Page design
Page design
2. Basics in Web Design
 Brief History of Internet
Brief History of Internet  What is World Wide Web
What is World Wide Web  Why create a web site
Why create a web site  Web Standards
Web Standards  Audience requirement.
Audience requirement.
3. Introduction to HTML
 What is HTML
What is HTML  HTML Documents
HTML Documents  Basic structure of an HTML document
Basic structure of an HTML document  Creating an HTML document
Creating an HTML document  Mark up Tags
Mark up Tags  Heading-Paragraphs
Heading-Paragraphs Line Breaks
Line Breaks  HTML Tags.
HTML Tags.
 Introduction to elements of HTML
Introduction to elements of HTML  Working with Text
Working with Text  Working with Lists, Tables and Frames
Working with Lists, Tables and Frames  Working with Hyperlinks, Images and Multimedia
Working with Hyperlinks, Images and Multimedia Working with Forms and controls.
Working with Forms and controls.
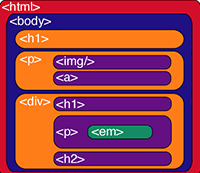
5. Introduction to Cascading Style Sheets
 Concept of CSS
Concept of CSS  Creating Style Sheet
Creating Style Sheet  CSS Properties
CSS Properties  CSS Styling(Background, Text Format, Controlling Fonts)
CSS Styling(Background, Text Format, Controlling Fonts)  Working with block elements and objects
Working with block elements and objects  Working with Lists and Tables
Working with Lists and Tables  CSS Id and Class
CSS Id and Class
 Box Model(Introduction, Border properties, Padding
Properties, Margin properties)
Box Model(Introduction, Border properties, Padding
Properties, Margin properties)  CSS Advanced(Grouping, Dimension, Display
,
Positioning, Floating, Align,Pseudo class, Navigation Bar,
Image Sprites, Attribute sector)
CSS Advanced(Grouping, Dimension, Display
,
Positioning, Floating, Align,Pseudo class, Navigation Bar,
Image Sprites, Attribute sector)  CSS Color
CSS Color  Creating page Layout and Site Designs.
Creating page Layout and Site Designs.
6. Introduction to Web Publishing or Hosting
 Creating the Web Site
Creating the Web Site  Saving the site
Saving the site  Working on the web site
Working on the web site  Creating web site structure
Creating web site structure  Creating Titles for web pages
Creating Titles for web pages  Themes-Publishing web sites.
Themes-Publishing web sites.
Adobe Flash Course Syllabus
A Quick Flash Demo
 Introducing the Flash Interface
Introducing the Flash Interface  Adding Elements to the Stage
Adding Elements to the Stage  Duplicating Library Items
Duplicating Library Items  Introducing Keyframes, the Transform Tool & Tweening
Introducing Keyframes, the Transform Tool & Tweening
 Creating Animations
Creating Animations  Adding Audio, Swapping Symbols & Testing a Movie
Adding Audio, Swapping Symbols & Testing a Movie
 Using Graphic Symbols
Using Graphic Symbols  Combining Animations into One Project
Combining Animations into One Project  Creating & Arranging Buttons
Creating & Arranging Buttons  Adding & Labeling Action Keyframes
Adding & Labeling Action Keyframes  Adding Behaviors to Buttons
Adding Behaviors to Buttons  Using the Publish Preview Command
Using the Publish Preview Command
Meet Flash: Fundamentals
 Navigating the Stage Area
Navigating the Stage Area  Accessing & Organizing Panels
Accessing & Organizing Panels  Saving, Exporting & Testing
Saving, Exporting & Testing  Selecting a Flash Player Version for a New Project
Selecting a Flash Player Version for a New Project  Introducing Layers
Introducing Layers  Creating New Layers & Moving Items Between Layers
Creating New Layers & Moving Items Between Layers  Customizing Keyboard Shortcuts & Locking Layers • Using Outline Mode, Layer Folders &Properties
Customizing Keyboard Shortcuts & Locking Layers • Using Outline Mode, Layer Folders &Properties
 Comparing Vectors & Bitmaps
Comparing Vectors & Bitmaps
 Working with the Pen Tool
Working with the Pen Tool
 Drawing a Heart Shape with the Pen Tool
Drawing a Heart Shape with the Pen Tool
 Where to Put Points & How Far to Drag Handles
Where to Put Points & How Far to Drag Handles
 Practicing Your Vector Drawing Skills
Practicing Your Vector Drawing Skills
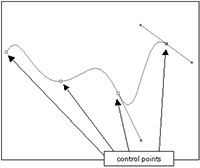
Flash Natural Drawing Tools
 Setting Up the Drawing Preferences
Setting Up the Drawing Preferences  Exploring the Pencil Tool Options
Exploring the Pencil Tool Options  Using the Line & Paint Bucket Tools
Using the Line & Paint Bucket Tools  Distinguishing Between Strokes & Fills
Distinguishing Between Strokes & Fills  Modifying Vectors Using the Selection Tool
Modifying Vectors Using the Selection Tool  Snapping & Modifying Curves with the Selection Tool
Snapping & Modifying Curves with the Selection Tool  Altering Drawings with the Selection Options
Altering Drawings with the Selection Options  Using the Brush & Paint Bucket Tools to Fill
Using the Brush & Paint Bucket Tools to Fill
 Painting Using the Various Brush Modes.
Painting Using the Various Brush Modes.
 Working with a Stylus & a Tablet
Working with a Stylus & a Tablet
 Drawing with the Rectangle Tool
Drawing with the Rectangle Tool
 Drawing with the Oval Tool
Drawing with the Oval Tool
 Drawing with the PolyStar Tool
Drawing with the PolyStar Tool
 Working with the Eye Dropper Tool
Working with the Eye Dropper Tool
 Working with the Ink Bottle Tool
Working with the Ink Bottle Tool
 Working with the Eraser Tool
Working with the Eraser Tool
Advanced Vector Drawing
 Intersecting Shapes within a Single Layer
Intersecting Shapes within a Single Layer  Using the Selection Tool
Using the Selection Tool  Creating Complex Shapes with Intersecting Lines
Creating Complex Shapes with Intersecting Lines
 Combining Tools to Create Detailed Curves
Combining Tools to Create Detailed Curves  Vector Drawing Techniques
Vector Drawing Techniques  Grouping Vector Shapes
Grouping Vector Shapes  Creating & Arranging Groups
Creating & Arranging Groups  Object-Based Drawing
Object-Based Drawing
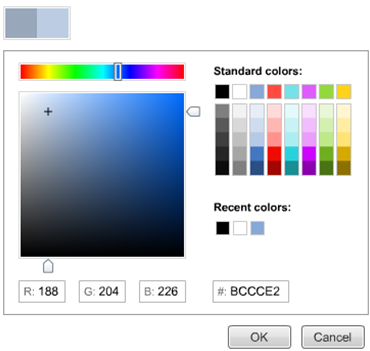
 Introducing Advanced Color Selection
Introducing Advanced Color Selection  Working with the Color Mixer
Working with the Color Mixer Creating Transparency & Sampling Colors
Creating Transparency & Sampling Colors  Using the Color Swatches Palette
Using the Color Swatches Palette  Applying & Stylizing Strokes
Applying & Stylizing Strokes
 Adjusting Cap, Join & Other Stroke Properties
Adjusting Cap, Join & Other Stroke Properties  Applying & Transforming Gradients
Applying & Transforming Gradients  Saving & Locking Gradients
Saving & Locking Gradients  Choosing a Gradient Overflow
Choosing a Gradient Overflow  Adding Transparency to a Gradient
Adding Transparency to a Gradient
Bitmaps in Flash
 Importing Files to the Stage & Library
Importing Files to the Stage & Library  File Compression Settings, Size Report & Use Count
File Compression Settings, Size Report & Use Count  Compressing Individual Files
Compressing Individual Files  Importing an Image with a Transparent Background
Importing an Image with a Transparent Background  Using Trace Bitmap to Change a Background to Vectors
Using Trace Bitmap to Change a Background to Vectors  Changing a Foreground Item to Vectors
Changing a Foreground Item to Vectors  Using the Optimize Curves Command
Using the Optimize Curves Command  Grouping an Image & Using the Transform Tools
Grouping an Image & Using the Transform Tools  Performing Transformations Numerically
Performing Transformations Numerically  Working with the Free Transform Options
Working with the Free Transform Options  Working with Bitmap Fills inside a Vector Shape
Working with Bitmap Fills inside a Vector Shape  Using the Break Apart Command & the Magic Wand Tool
Using the Break Apart Command & the Magic Wand Tool
Using Text in Flash
 Auto-Sizing, Auto-Wrapping & Selecting Text
Auto-Sizing, Auto-Wrapping & Selecting Text
 Changing a Font, Picking a Color & Checking Spelling
Changing a Font, Picking a Color & Checking Spelling
 Using Rulers, Guides, Grids & Snapping
Using Rulers, Guides, Grids & Snapping
 Aligning, Distributing & Spacing Text
Aligning, Distributing & Spacing Text
 Working with Device Fonts
Working with Device Fonts
 Editing Files with Missing Fonts
Editing Files with Missing Fonts
 Anti-Aliasing Text for Better Quality & Readability
Anti-Aliasing Text for Better Quality & Readability
 Paragraph & Character Formatting
Paragraph & Character Formatting
 Using Text as a Design Element. Text on a Path, Guide Layers & the Transform Panel
Using Text as a Design Element. Text on a Path, Guide Layers & the Transform Panel
 Introducing Symbols
Introducing Symbols  Creating & Reusing a Symbol
Creating & Reusing a Symbol  Editing a Symbol in Place
Editing a Symbol in Place  Editing a Symbol in the Library
Editing a Symbol in the Library  Modifying an Instance of a Symbol
Modifying an Instance of a Symbol  Nesting Elements inside a Symbol
Nesting Elements inside a Symbol
 Adjusting the Color & Opacity of a Symbol
Adjusting the Color & Opacity of a Symbol  Deconstructing & Reordering Symbol Parts
Deconstructing & Reordering Symbol Parts  Taking Advantage of Logically Ordered Layers
Taking Advantage of Logically Ordered Layers  Organizing the Library
Organizing the Library  Looking at Symbols as a Movie inside of a Movie
Looking at Symbols as a Movie inside of a Movie

BookSymbol Effects: Filters & Blends
 Applying Fader Gradients
Applying Fader Gradients  Adding Text & Graphics to a Background
Adding Text & Graphics to a Background  Converting Text to Symbols
Converting Text to Symbols  Using Drop Shadows with Text
Using Drop Shadows with Text  Using Drop Shadows with Symbols
Using Drop Shadows with Symbols  Applying the Blur Filter to Text & Symbols
Applying the Blur Filter to Text & Symbols  Customizing Glow & Bevel
Customizing Glow & Bevel  Disabling Filters & Using the Gradient Bevel Filter
Disabling Filters & Using the Gradient Bevel Filter  Stacking Order & Other Filters & Settings
Stacking Order & Other Filters & Settings
 Saving & Using Filter Presets
Saving & Using Filter Presets  Understanding Blend Modes
Understanding Blend Modes  Using the Normal, Darken & Multiply Blend Modes
Using the Normal, Darken & Multiply Blend Modes Using the Lighten & Screen Blend Modes
Using the Lighten & Screen Blend Modes  Using the Overlay & Hard Light Blend Modes
Using the Overlay & Hard Light Blend Modes  Using the Add, Subtract, Difference & Invert Blends
Using the Add, Subtract, Difference & Invert Blends  Building a Mask without Blend Modes
Building a Mask without Blend Modes  Building a Mask Using Alpha, Blend & Layer Modes
Building a Mask Using Alpha, Blend & Layer Modes
Introduction to the Timeline
 Introducing Frame-Based Animation
Introducing Frame-Based Animation  The Timeline Window
The Timeline Window  Understanding Keyframes
Understanding Keyframes Animating Your Elements Using Keyframes
Animating Your Elements Using Keyframes  Practicing Your Animation Techniques
Practicing Your Animation Techniques  Using Onion Skin View
Using Onion Skin View  Facial Animation
Facial Animation  Replacement Animation
Replacement Animation  Rotoscoping
Rotoscoping
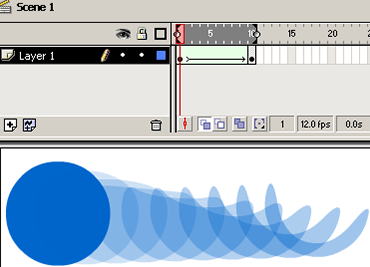
 Doing a Simple Shape Tween
Doing a Simple Shape Tween Getting Your Tween to Behave Properly
Getting Your Tween to Behave Properly Distributive & Angular Blending
Distributive & Angular Blending  Working with Shape Hints
Working with Shape Hints
 Modifying a Graphic for a Better Tween
Modifying a Graphic for a Better Tween  Choosing Shape Hint Location for a Complex Graphic
Choosing Shape Hint Location for a Complex Graphic  Segmenting a Graphic for Smoother Tweening
Segmenting a Graphic for Smoother Tweening Tweening Facial Expressions
Tweening Facial Expressions
Motion Tweening
 Differences in Structure of Shape & Motion Tweens
Differences in Structure of Shape & Motion Tweens  Converting an Object to Symbol & Motion Tweening
Converting an Object to Symbol & Motion Tweening  Scaling & Rotating Motion Tweening
Scaling & Rotating Motion Tweening  Adding a Background Color & Making a Cloud Layer
Adding a Background Color & Making a Cloud Layer  The Problems with Motion Tweening a Shape
The Problems with Motion Tweening a Shape  Problems with Using the Create Motion Tween Option
Problems with Using the Create Motion Tween Option  Setting Up the Traveling Cloud Animation
Setting Up the Traveling Cloud Animation  Simulating the Camera Flying Down to the Ground
Simulating the Camera Flying Down to the Ground  Animating the Airship Landing
Animating the Airship Landing  Creating an Elastic Landing Effect
Creating an Elastic Landing Effect  Replacing Grouped Ship with Ship & Canopy
Replacing Grouped Ship with Ship & Canopy  Animating the Alien Hopping out of the Ship
Animating the Alien Hopping out of the Ship  Motion Tweening Individual Text Characters
Motion Tweening Individual Text Characters  Adding Randomness to Text Animations
Adding Randomness to Text Animations
Advanced Animation Techniques
 Fading In a Background
Fading In a Background  Animating a Banner with Filters & Text
Animating a Banner with Filters & Text  Animating a Title with a Blur Effect
Animating a Title with a Blur Effect  Animating Navigation Buttons into View
Animating Navigation Buttons into View  Fading In a Block of Text
Fading In a Block of Text  Tweaking the Timing of Animations
Tweaking the Timing of Animations  Setting Up a Motion Guide Path
Setting Up a Motion Guide Path  Orienting an Object to a Motion Guide Path
Orienting an Object to a Motion Guide Path  Controlling Speed, Snapping & Registration Point
Controlling Speed, Snapping & Registration Point  Reconfiguring Your Workspace
Reconfiguring Your Workspace  Adding & Swapping Facial Expression Symbols.
Adding & Swapping Facial Expression Symbols.  Modifying Elements to React with One Another
Modifying Elements to React with One Another  Creating a Stretch & Squash Effect
Creating a Stretch & Squash Effect  Tweening & Shifting Keyframes to Exaggerate Motion
Tweening & Shifting Keyframes to Exaggerate Motion
 Understanding Speed in Flash
Understanding Speed in Flash  Introducing Ease
Introducing Ease  Easing In & Out of Motion Tweens
Easing In & Out of Motion Tweens  Improving Animations with Subtle Ease
Improving Animations with Subtle Ease  Using the Custom Ease In / Ease Out Dialog Box
Using the Custom Ease In / Ease Out Dialog Box
 Easing within a Motion Guide Layer
Easing within a Motion Guide Layer  Customizing Ease for Position
Customizing Ease for Position  Customizing Ease for Rotation & Color
Customizing Ease for Rotation & Color  Using a Gradient to Simulate Speed
Using a Gradient to Simulate Speed  Applying a Motion Blur to Simulate Speed
Applying a Motion Blur to Simulate Speed
Motion Tweening Nesting Symbols for Complex Animation
 Introducing Timeline Effects
Introducing Timeline Effects  Reviewing & Preparing for Animation
Reviewing & Preparing for Animation  Working with Groups & Symbols
Working with Groups & Symbols  Symbols, Nesting & Motion Tweening
Symbols, Nesting & Motion Tweening  Creating Nested Animations
Creating Nested Animations  Building Multi-Layered Animations
Building Multi-Layered Animations Creating Motion along a Path
Creating Motion along a Path  Packaging Symbols
Packaging Symbols  Understanding Graphic & Movie Clip Symbols
Understanding Graphic & Movie Clip Symbols Creating Character Animations
Creating Character Animations  Managing Character Animations with Nesting & Symbols
Managing Character Animations with Nesting & Symbols
Animated Masks and Filters
 Using Open External Library to Copy Assets
Using Open External Library to Copy Assets
 Animating a Mask Using a Shape Tween
Animating a Mask Using a Shape Tween
 Creating a Magnifying Glass Effect
Creating a Magnifying Glass Effect
 Animating a Signature Using Stage Reveal
Animating a Signature Using Stage Reveal
 Working with Complex, Layered Vector Artwork
Working with Complex, Layered Vector Artwork
 Reproducing an Adobe® Illustrator® Gradient
Reproducing an Adobe® Illustrator® Gradient
 Animating a Gradient to Create a Shimmer Effect
Animating a Gradient to Create a Shimmer Effect
 Combining Filters, Blends & Motion Tweening
Combining Filters, Blends & Motion Tweening
 Creating a Kaleidoscope Effect
Creating a Kaleidoscope Effect
 Creating a Realistic Drop Shadow
Creating a Realistic Drop Shadow
 Using Blend Options to Create a Soft Mask
Using Blend Options to Create a Soft Mask

 Importing & Adding Sound to the Timeline
Importing & Adding Sound to the Timeline  Working with Audio File Sizes
Working with Audio File Sizes  Adding Effects to Sound & Customizing Settings
Adding Effects to Sound & Customizing Settings  Syncing Up the Sound with the Action
Syncing Up the Sound with the Action  Working with Speech Compression
Working with Speech Compression  Streaming Audio
Streaming Audio  Working with Frame Labels
Working with Frame Labels  Adjusting the Animation to the Voice Over Track
Adjusting the Animation to the Voice Over Track  Setting Up Audio for Lip Sync
Setting Up Audio for Lip Sync
 Adding a Looping Mouth Movie
Adding a Looping Mouth Movie  Fine-Tuning Specific Mouth Movements
Fine-Tuning Specific Mouth Movements Changing Facial Expressions to Match Words
Changing Facial Expressions to Match Words  Importing Video
Importing Video  Editing Video Prior to Bringing it into the Timeline
Editing Video Prior to Bringing it into the Timeline  Selecting Video Compression Settings
Selecting Video Compression Settings  Adding Effects & Motion Tweens to Video
Adding Effects & Motion Tweens to Video  Using Progressive Download & Selecting the Skin
Using Progressive Download & Selecting the Skin Using the Flash 8 Video Encoder
Using the Flash 8 Video Encoder
Flash Buttons
 Making a Simple Button
Making a Simple Button  Using a Hit State
Using a Hit State  Making Animated Buttons
Making Animated Buttons  Adding Sounds to Buttons
Adding Sounds to Buttons  Applying a Drop Shadow
Applying a Drop Shadow  Making Buttons Using Bitmaps
Making Buttons Using Bitmaps  Using Blend Effects to Spice Up Your Buttons
Using Blend Effects to Spice Up Your Buttons  Adding a Message with the Status Bar Feature
Adding a Message with the Status Bar Feature  Using Buttons from the Common Libraries
Using Buttons from the Common Libraries  Using Rollovers to Display Images & Text
Using Rollovers to Display Images & Text
Scripting Basics
 Setting Up to Use Action Script
Setting Up to Use Action Script
 Introducing the Actions Window & Script Assist
Introducing the Actions Window & Script Assist
 Creating Buttons to Activate Action Script
Creating Buttons to Activate Action Script
 Labeling Buttons in the Properties Window
Labeling Buttons in the Properties Window
 Assigning Play & Stop Actions to Buttons
Assigning Play & Stop Actions to Buttons
 Organizing & Arranging Buttons
Organizing & Arranging Buttons
 Using the Behaviors Window to Stop All Sounds
Using the Behaviors Window to Stop All Sounds
 Using the Goto and Play Behavior
Using the Goto and Play Behavior
 Modifying a Behavior & Adding an Action Layer.
Modifying a Behavior & Adding an Action Layer.
 Duplicating & Modifying Sequences in the Timeline
Duplicating & Modifying Sequences in the Timeline
 Using Advanced Goto Behavior Options
Using Advanced Goto Behavior Options
 Linking a Button to a Web
Linking a Button to a Web
 Dividing Movies into Scenes
Dividing Movies into Scenes Arranging & Adding Scenes in the Scene Panel
Arranging & Adding Scenes in the Scene Panel Creating a New Scene from a Copy
Creating a New Scene from a Copy  Adding Stop Action Scripts to Flash Scenes
Adding Stop Action Scripts to Flash Scenes  Setting Up a Basic Navigation System
Setting Up a Basic Navigation System  Using a Generic Action Script for More Flexible Navigation
Using a Generic Action Script for More Flexible Navigation
 Creating a Non-Linear Navigation System
Creating a Non-Linear Navigation System  Navigating with Keyframe Labels
Navigating with Keyframe Labels  Navigating with Separate Flash Files
Navigating with Separate Flash Files  Loading an External Movie inside of a Symbol
Loading an External Movie inside of a Symbol  Loading External Images inside of a Symbol
Loading External Images inside of a Symbol

 Setting Up a Slide Presentation
Setting Up a Slide Presentation  Adding Content & Creating New Slides
Adding Content & Creating New Slides  Nesting, Navigating, Arranging & Naming Slides
Nesting, Navigating, Arranging & Naming Slides  Adding Filters & Text to Slides
Adding Filters & Text to Slides  Adding & Resizing Navigation Buttons from the Library
Adding & Resizing Navigation Buttons from the Library  Assigning Behaviors to Screen Buttons
Assigning Behaviors to Screen Buttons
 Exploring & Editing Button Layers
Exploring & Editing Button Layers  Using Transitions with Screens
Using Transitions with Screens  Screens vs. Forms. Setting Form Parameters & Navigation.
Screens vs. Forms. Setting Form Parameters & Navigation.  Introducing Templates
Introducing Templates  Using the Quiz Style Template
Using the Quiz Style Template  Publishing Movie
Publishing Movie
 choosing a workspace
choosing a workspace document window & toolbars
document window & toolbars the document window
the document window the launcher
the launcher the insert panel & tool sets
the insert panel & tool sets the document toolbar
the document toolbar the property inspector
the property inspector dockable floating panels
dockable floating panels using contextual menus
using contextual menus
 defining a site
defining a site file and folder management
file and folder management creating site maps
creating site maps using the file browser
using the file browser create a site from nothing
create a site from nothing

 defining the site
defining the site creating and saving documents
creating and saving documents inserting images with assets panel
inserting images with assets panel adding text
adding text aligning page elements
aligning page elements modifying page properties
modifying page properties creating links with text and images
creating links with text and images adding keyword & description meta tags
adding keyword & description meta tags preview in browser
preview in browser define a secondary browser
define a secondary browser
 link with point to file
link with point to file linking to new source files
linking to new source files browse for file and link history
browse for file and link history anchor links
anchor links email links
email links file links
file links imagemaps
imagemaps
 html text formatting
html text formatting font lists
font lists text alignment
text alignment html lists
html lists color schemes
color schemes text in tables
text in tables flash text
flash text character objects
character objects
 insert and modify a table
insert and modify a table
 fixed width tables
fixed width tables
 relative width tables
relative width tables
 hybrid table
hybrid table
 insert tabular data
insert tabular data
 sort table data
sort table data
 simple rollovers - insert rollover
simple rollovers - insert rollover simple rollover - swap image behavior
simple rollover - swap image behavior multiple-event rollovers
multiple-event rollovers flash buttons
flash buttons
 redefining HTML tags
redefining HTML tags defining a custom class
defining a custom class CSS selectors
CSS selectors CSS selectors to group tags
CSS selectors to group tags linking to external CSS
linking to external CSS CSS reference panel
CSS reference panel
 editing in the code view
editing in the code view code view options
code view options quick tag editor & attribute hints
quick tag editor & attribute hints cleanup HTML
cleanup HTML cleanup word HTML
cleanup word HTML code validator / XHTML
code validator / XHTML
 form objects
form objects
 creating a form
creating a form
 creating a jump menu
creating a jump menu

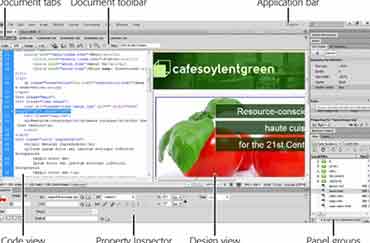
 set text of status bar
set text of status bar open browser window behavior
open browser window behavior downloading and installing extensions
downloading and installing extensions
 history panel
history panel copy / paste history
copy / paste history create web photo album
create web photo album
 templates in action
templates in action creating / modifying templates
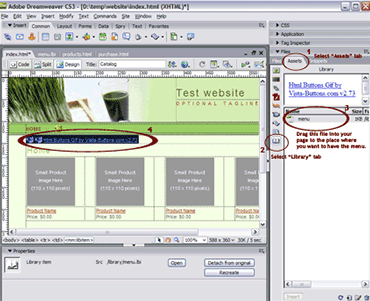
creating / modifying templates library items in action
library items in action creating / modifying library items
creating / modifying library items
 linking to sounds
linking to sounds
 embedding sounds
embedding sounds
 inserting flash content
inserting flash content
 inserting director content
inserting director content
 inserting a quicktime movie
inserting a quicktime movie
 putting files to the web server
putting files to the web server
[E]. JAVA COURSE
| 1.Introduction to java programming language |
 Key features of java technology Key features of java technology |
 Creating and using sample java class program Creating and using sample java class program |
 Compling the java program Compling the java program |
| 2.Beginning to program with java programming |
 Declairing,initializing and using variables Declairing,initializing and using variables |
 Datatypes in java,Operators,Type casting Datatypes in java,Operators,Type casting |
| 3.Use of decision making constructs |
 If,If else, Nested If,Switch If,If else, Nested If,Switch |
| 4.Use of loop constructs |
 for,while, do-while,Jumps in loops(Break,continue) for,while, do-while,Jumps in loops(Break,continue) |
| 5.KeyBoard Input |
| 6.Developing and using methods |
 Creating and invoking methods Creating and invoking methods
|
 Passing Arguments and Returning Values Passing Arguments and Returning Values |
 Creating static Methods and Variables Creating static Methods and Variables |
 Using method overloading Using method overloading |
| 7.Classes and objects |
 Programs, access modifiers Programs, access modifiers |
| 8.Constructors |
 creating constructors creating constructors |
| 9.Creating and using Arrays |
 creating One-dimensional Arrays creating One-dimensional Arrays |
 Setting Array values using length attribute and loop Setting Array values using length attribute and loop |
 creating two dimensional array creating two dimensional array |
| 10.Vectors |
| 11.String Handling |
 String class,String Buffer class String class,String Buffer class |
| 12.Inheritance |
| 13.Exception Handling |
 Exception types, try, catch, finally, throw, throws Exception types, try, catch, finally, throw, throws |
| 14.MultiThreading |
 Thread Priorities,Creating threads using different methods Thread Priorities,Creating threads using different methods |
 Thread synchronization Thread synchronization |
| 15.Interface |
| 16.Applets |
 Applet skeleton,html applet tag,simple programs Applet skeleton,html applet tag,simple programs |
| 17.Event Handling |
| 18.Event Source,Event Listener(key board,mouse) |
| 19.AWT Controls |
 Labels,Buttons,check boxes,choice list Labels,Buttons,check boxes,choice list |
 scroll bars,text box,tet area,menu scroll bars,text box,tet area,menu |
| 20.Layoutmanager(Flow,border,grid,grid bag,cardlayout) |
[F]. J2EE COURSE
1. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
- a. Getting the example to work
- Step 1: Find the JDBC Driver
- Step 2: Configure the database
- Step 3: Test the configuration
- Step 4: Generate your SQL query
- Step 5: Modify and paste in your query
- b. A GUI version of the lookup program
- c. Why the JDBC API seems so complex
- d. A more sophisticated example
2. RMI (Remote Method Invocation)
- a. Remote interfaces
- b. Implementing the remote interface
- c. Setting up the registry
- d. Creating stubs and skeletons
- e. Using the remote object
- a. CORBA fundamentals
- b. CORBA Interface Definition Language (IDL)
- c. The naming service
- d. Writing the IDL source
- e. Creating stubs and skeletons
- f. Implementing the server and the client
- g. Some CORBA services
- h. Activating the name service process
- i. Activating the server and the client
- j. Java Applets and CORBA
- k. CORBA vs. RMI
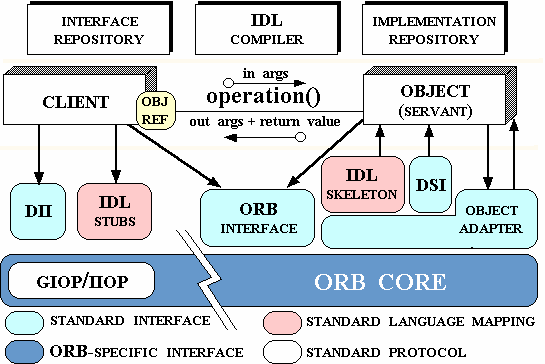
4. Network programming
- a. Identifying a machine
- b. Servers and clients
- c. Testing programs without a network
- d. Port: a unique place within the machine
5. Servlets
- a. The basic servlet
- b. Servlets and multithreading
- c. Handling sessions with servlets
- d. The Cookie class
- e. The Session class
- f. Running the servlet examples
6. Java Server Pages
- a. Implicit objects
- b. JSP directives
- c. JSP scripting elements
- d. Extracting fields and values
- e. JSP page attributes and scope
- f. Manipulating sessions in JSP
- g. Creating and modifying cookies
- h. JSP summary
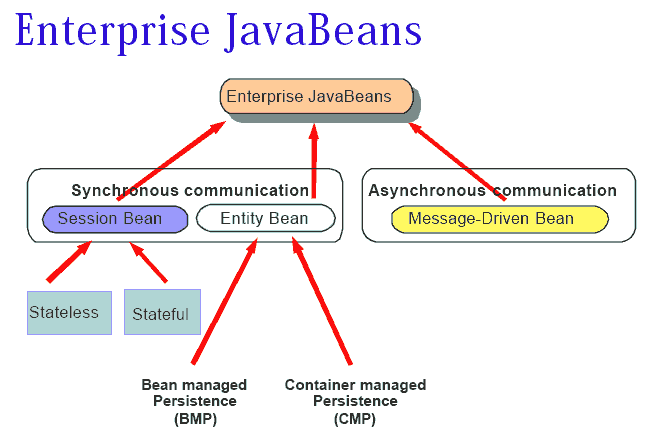
- a. JavaBeans vs. EJBs
- b. The EJB specification
- c. EJB components
- d. EJB Container & Server
- e. Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI)
- f. Java Transaction API/Java Transaction Service (JTA/JTS)
- g. CORBA and RMI/IIOP
- h. The pieces of an EJB component
- i. Enterprise Bean
- j. Home interface
- k. Remote interface
- l. Deployment descriptor
- m. EJB-Jar file, EJB Operation
- o. Types of EJBs
- r. Developing an EJB
8. XML
- a. XML Introduction
 XML Tree
XML Tree XML Syntax
XML Syntax XML Elements
XML Elements XML Attributes
XML Attributes XML Validation
XML Validation XML Validator
XML Validator XML Viewing
XML Viewing XML CSS
XML CSS XML XSLT
XML XSLT
- b. XML JavaScript
 XML HTTP Request
XML HTTP Request XML Parser
XML Parser XML DOM
XML DOM XML to HTML
XML to HTML XML Applications
XML Applications
- c. XML Advanced
 XML Namespaces
XML Namespaces XML CDATA
XML CDATA XML Encoding
XML Encoding XML Server
XML Server XML DOM Advanced
XML DOM Advanced XML Don't
XML Don't XML Technologies
XML Technologies XML in Real Life
XML in Real Life XML Editors
XML Editors XML Summary
XML Summary
- a. Web Logic Introduction
- b. Weblogic Workshop
 File Types
File Types Applications and projects
Applications and projects Debugging application
Debugging application Managing build process
Managing build process Compiling
Compiling Source control systems
Source control systems Message logging
Message logging Developing web applications
Developing web applications
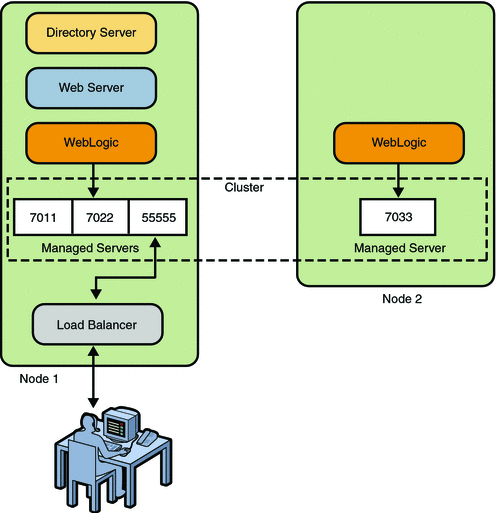
10. TOMCAT STRUTS
- a. Introduction
- b. Building Model Components
 JavaBeans and Scope
JavaBeans and Scope Action Form Beans
Action Form Beans System State Beans
System State Beans Business Logic Beans
Business Logic Beans- c. Building View Components
 Internationalization
Internationalization
 Forms and Form Bean Interactions
Forms and Form Bean Interactions Automatic Form Population
Automatic Form Population Automatic Form Validation
Automatic Form Validation The Struts Validator
The Struts Validator Page Composition With Tiles
Page Composition With Tiles Presentation Frameworks
Presentation Frameworks Direct Presentation Techniques
Direct Presentation Techniques Image Rendering Components
Image Rendering Components Rendering Text
Rendering Text
- d. Building Controller Components
 The ActionServlet
The ActionServlet ActionForm Classes
ActionForm Classes Action Classes
Action Classes  Exception Handler
Exception Handler Plugin Classes
Plugin Classes  The ActionMapping Implementation
The ActionMapping Implementation Writing ActionMappings
Writing ActionMappings  Using ActionMappings for Pages
Using ActionMappings for Pages Using Wildcards in ActionMappings
Using Wildcards in ActionMappings Using The Commons Logging Interface
Using The Commons Logging Interface- e. Configuring Applications
 The Configuration File
The Configuration File Configuring your application for modules
Configuring your application for modules The Web Application Deployment Descriptor
The Web Application Deployment Descriptor Add Framework Components To Your Application
Add Framework Components To Your Application Logging
Logging
[G]. .NET COURSE
| .Net 2008 Day wise plan(C#.net, vb.net) |
| Module 1: Introduction to .NET |
| Module 2: Introduction to .NET Framework 3.5 |
 Versions of Framework Versions of Framework |
 Benefits of Framework Benefits of Framework |
 Architecture of .NET Framework Architecture of .NET Framework |
 Components of .NET Framework Components of .NET Framework |
| Module 3: Creation of Console Application |
 Use of variables , data types Use of variables , data types |
 Operators Operators |
 Selection statements Selection statements |
 The if …else statement The if …else statement |
 The Select …. Case statement The Select …. Case statement |
 Iteration statement Iteration statement |
 The While …. End statement The While …. End statement |
 The While …. End statement The While …. End statement |
 The for … next statement The for … next statement |
 The for… each statement The for… each statement |
 Arrays Arrays |
 Enumeration Enumeration |
| Module 4: Object Oriented Programming |
 Classes and objects Classes and objects |
 Inheritance Inheritance |
 Interfaces Interfaces |
 Polymorphism Polymorphism |
 Anonymous types Anonymous types |
 Structures Structures |
 Name spaces Name spaces |
| Module 5: Creating the Windows form application |
 Working with all windows Form controls Working with all windows Form controls |
 Working with container controls Working with container controls |
 Working with menus control Working with menus control |
 Working with dialog boxes controls Working with dialog boxes controls |
| Module 6: Working with ADO.NET |
| Module 7: Working with Windows Presentation Foundation |
| Module 8: ASP.NET 3.5 essentials |
 Introduction to ASP.NET Introduction to ASP.NET
|
 Web form controls Web form controls |
 standard controls standard controls |
 navigation controls navigation controls |
 validationcontrols validationcontrols |
 login controls login controls |
 web part controls web part controls |
 implementing Master Pages and Themes implementing Master Pages and Themes |
 Caching in ASP.net Caching in ASP.net |
 Web service Web service |
[H]. DIPLOMA IN TESTING TOOLS
Brief Intraduction to Software Systems and SDLC
 Basic Testing Vocabulary
Basic Testing Vocabulary Quality Assurance versus Quality Control
Quality Assurance versus Quality Control The Cost of Quality
The Cost of Quality Software Quality Factors
Software Quality Factors How Quality is Defined
How Quality is Defined Why Do We Test Software?
Why Do We Test Software? What is a Defect?
What is a Defect? The Multiple Roles of the Software Tester(People Relationships)
The Multiple Roles of the Software Tester(People Relationships)
 Scope of Testing
Scope of Testing
 When Should Testing Occur?
When Should Testing Occur?
 Testing Constraints
Testing Constraints
 Life Cycle Testing
Life Cycle Testing
 Independent Testing
Independent Testing
 What is a QA Process?
What is a QA Process?
 Levels of Testing
Levels of Testing
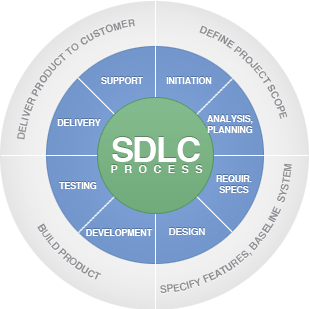
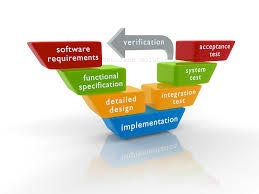
 The “V” Concept of Testing
The “V” Concept of Testing
- a. Testing Techniques
 Structural versus Functional Technique Categories
Structural versus Functional Technique Categories Verification versus Validation
Verification versus Validation Static versus Dynamic Testing
Static versus Dynamic Testing Examples of Specific Testing Techniques
Examples of Specific Testing Techniques
- b. Test Administration
 Test Planning
Test Planning  Customization of the Test Process
Customization of the Test Process  Budgeting
Budgeting  Scheduling
Scheduling
- c. Create the Test Plan
 Prerequisites to test planning
Prerequisites to test planning Understand the Characteristics of the Software Being Developed
Understand the Characteristics of the Software Being Developed Build the Test Plan
Build the Test Plan Write the Test Plan
Write the Test Plan
 Test Cases:
Test Cases:
 Test case Design
Test case Design
 Building test cases
Building test cases
 Test data mining
Test data mining
 Test execution
Test execution
 Test Reporting
Test Reporting
 Defect Management
Defect Management
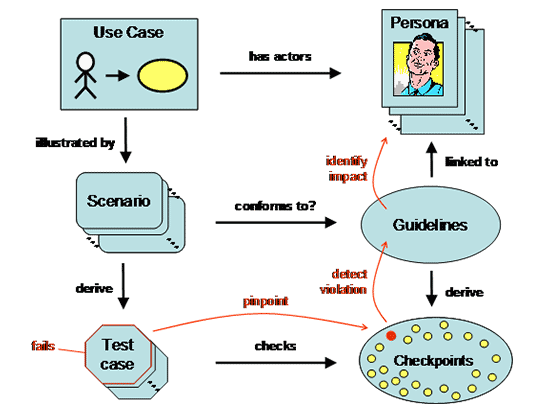
 Test Coverage – Traceability matrix
Test Coverage – Traceability matrix
- Test Metrics – Guidelines and usage
- Test reporting
 Guidelines for writing test reports
Guidelines for writing test reports
- a. Managing Change
 Software Configuration Management
Software Configuration Management Change Management
Change Management- b. Risks
 Risk Analysis and Management with examples
Risk Analysis and Management with examples
- c. User Acceptance testing
 in detail explanation with details
in detail explanation with details- d. Case Study
 How to test web, stand alone and database applications – with examples
How to test web, stand alone and database applications – with examples- e. Help with resume and testing interview skills
- f. Automation Testing Basics
 Basics of automation testing – why, when and how to perform automation testing
Basics of automation testing – why, when and how to perform automation testing Factors for choosing a particular tool
Factors for choosing a particular tool An overview for the major functional testing tools
An overview for the major functional testing tools Overview of Test management and bug tracking tools
Overview of Test management and bug tracking tools
[I]. BASIC ENGLISH
 Our Basic English classes help get you started with the basics in English and to create a foundation on which you can build upon. Basic English is for everyone and at this level we will teach an equal mixture of grammar, conversation and listening skills. This integrated approach will help prepare you for travel, work, and school. You will get your basics in English as well as some good conversational specifics. If you have any areas of weakness or specific areas which can be worked on, we will strive to help you to reach your target. We will analyze your improvement from time to time and will take a decision on taking you to the next level.
Our Basic English classes help get you started with the basics in English and to create a foundation on which you can build upon. Basic English is for everyone and at this level we will teach an equal mixture of grammar, conversation and listening skills. This integrated approach will help prepare you for travel, work, and school. You will get your basics in English as well as some good conversational specifics. If you have any areas of weakness or specific areas which can be worked on, we will strive to help you to reach your target. We will analyze your improvement from time to time and will take a decision on taking you to the next level.

 Vocabulary
Vocabulary Pronunciation
Pronunciation Grammar
Grammar Expression Skills
Expression Skills Conversation
Conversation
 Reading
Reading Writing
Writing Group Discussions
Group Discussions Public Speaking
Public Speaking Seminars
Seminars
[J]. INTERMEDIATE ENGLISH
 Many people fall into the Intermediate Category. In this level we review the foundation of the Beginner Level and start adding more vocabulary, more complicated grammatical rules, reading, writing, as well as trying to improve the pace of conversation, pronunciation and accent. You will start to read more and will have conversations at a more normal pace in English. At this level we want you to feel comfortable in thinking in English and speaking in the moment. In Intermediate English classes we use an integrated approach often mixed with current issues articles, stories and conversation
Many people fall into the Intermediate Category. In this level we review the foundation of the Beginner Level and start adding more vocabulary, more complicated grammatical rules, reading, writing, as well as trying to improve the pace of conversation, pronunciation and accent. You will start to read more and will have conversations at a more normal pace in English. At this level we want you to feel comfortable in thinking in English and speaking in the moment. In Intermediate English classes we use an integrated approach often mixed with current issues articles, stories and conversation
 Vocabulary
Vocabulary Expression SkillsS
Expression SkillsS Grammar Pronunciation
Grammar Pronunciation- Personality & Fluency Development
 Conversation
Conversation Public & Effective Speaking
Public & Effective Speaking Formal & Informal Speaking
Formal & Informal Speaking Group Discussions & Seminars.
Group Discussions & Seminars.

[K]. ADVANCE ENGLISH
 Our Advanced English module helps you gain fluency. We focus a lot on reading, writing, and speaking. This class helps you prepare for any Fluency certification or allows you to speak and understand English at a normal pace. We prepare students for International Certification, as well as any university class or translation class that you may need. We use practice exams as well as essay writing and practice readings, we also give oral exams and mock interviews to help you prepare for the exams you need to pass. We use an integrated approach suited to your specific requirements.
Our Advanced English module helps you gain fluency. We focus a lot on reading, writing, and speaking. This class helps you prepare for any Fluency certification or allows you to speak and understand English at a normal pace. We prepare students for International Certification, as well as any university class or translation class that you may need. We use practice exams as well as essay writing and practice readings, we also give oral exams and mock interviews to help you prepare for the exams you need to pass. We use an integrated approach suited to your specific requirements.
 Introduction to 3D Animation Phonetics
Introduction to 3D Animation Phonetics Effective Expressions
Effective Expressions Epigrammatic Speech
Epigrammatic Speech Humour, Sarcasm and Wit
Humour, Sarcasm and Wit Group Discussions
Group Discussions Language for marketing and sales
Language for marketing and sales
 Seminars and presentations
Seminars and presentations
 Compering
Compering Emceeing
Emceeing Various shades of speech that include brevity, coherence and clarity
Various shades of speech that include brevity, coherence and clarity Personality development
Personality development
