
About Advanced Java Course Training
This course is aimed at the professionals who want to Specialize in Java Technologies. As java is Platform independent it is preferred by most of the Technical experts as the perfect tool for developing the Solutions for todays complex computing requirements.
Our advanced Java course comprises basic and advanced subjects. Our Java course has been designed to take place in good MNC companies as soon as you finish our Diginet Infosystems Java certification. Our Java Trainers are Java-certified experts with knowledge of various Java projects in real time. In order to achieve the career goals of all people, we developed our Java course contents and curriculum. You will be trained on Java Script and Java Programme, Java Speech, Basic Java Programme, Java OOPS Categories, Java Classes, Packages, Swing, Java Real Time Project and Java Placement Training in our Java Training Programmes.
ADVANCED JAVA COURSE HIGHLIGHTS
Advanced Java Course Duration
4 Month
(3 Months course and 1 month Project)
Learners
50000
Delivery Mode
Classroom Training
Apply Online
ADVANCED JAVA COURSE OUTCOME

ADVANCED JAVA
 Placing the Java EE Model in Context
Placing the Java EE Model in Context Java EE 5 technology addresses these needs
Java EE 5 technology addresses these needs
1. Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)
- a. Getting the example to work
- Step 1: Find the JDBC Driver
- Step 2: Configure the database
- Step 3: Test the configuration
- Step 4: Generate your SQL query
- Step 5: Modify and paste in your query
- b. A GUI version of the lookup program
- c. Why the JDBC API seems so complex
- d. A more sophisticated example
2. RMI (Remote Method Invocation)
- a. Remote interfaces
- b. Implementing the remote interface
- c. Setting up the registry
- d. Creating stubs and skeletons
- e. Using the remote object
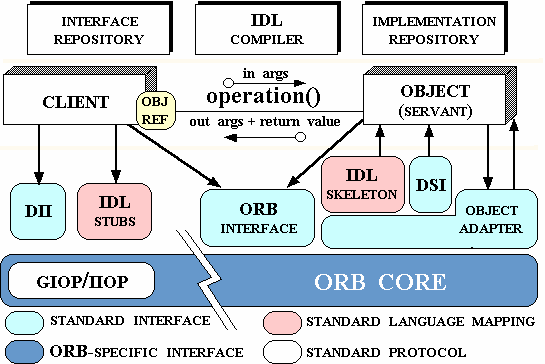
- a. CORBA fundamentals
- b. CORBA Interface Definition Language (IDL)
- c. The naming service
- d. Writing the IDL source
- e. Creating stubs and skeletons
- f. Implementing the server and the client
- g. Some CORBA services
- h. Activating the name service process
- i. Activating the server and the client
- j. Java Applets and CORBA
- k. CORBA vs. RMI
4. Network programming
- a. Identifying a machine
- b. Servers and clients
- c. Testing programs without a network
- d. Port: a unique place within the machine
5. Servlets
- a. The basic servlet
- b. Servlets and multithreading
- c. Handling sessions with servlets
- d. The Cookie class
- e. The Session class
- f. Running the servlet examples
6. Java Server Pages
- a. Implicit objects
- b. JSP directives
- c. JSP scripting elements
- d. Extracting fields and values
- e. JSP page attributes and scope
- f. Manipulating sessions in JSP
- g. Creating and modifying cookies
- h. JSP summary
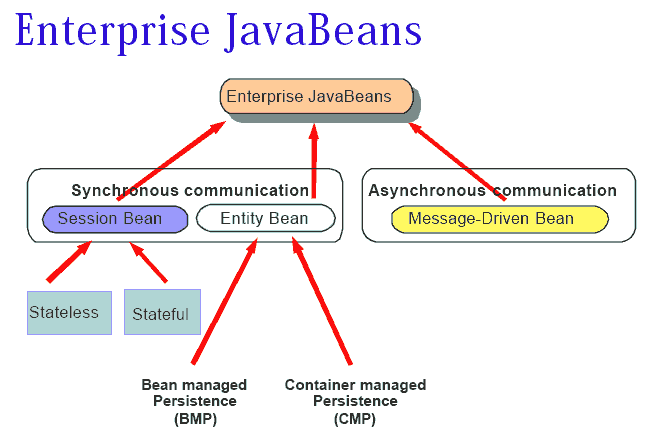
- a. JavaBeans vs. EJBs
- b. The EJB specification
- c. EJB components
- d. EJB Container & Server
- e. Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI)
- f. Java Transaction API/Java Transaction Service (JTA/JTS)
- g. CORBA and RMI/IIOP
- h. The pieces of an EJB component
- i. Enterprise Bean
- j. Home interface
- k. Remote interface
- l. Deployment descriptor
- m. EJB-Jar file, EJB Operation
- o. Types of EJBs
- r. Developing an EJB
8. XML
- a. XML Introduction
 XML Tree
XML Tree XML Syntax
XML Syntax XML Elements
XML Elements XML Attributes
XML Attributes XML Validation
XML Validation XML Validator
XML Validator XML Viewing
XML Viewing XML CSS
XML CSS XML XSLT
XML XSLT
- b. XML JavaScript
 XML HTTP Request
XML HTTP Request XML Parser
XML Parser XML DOM
XML DOM XML to HTML
XML to HTML XML Applications
XML Applications
- c. XML Advanced
 XML Namespaces
XML Namespaces XML CDATA
XML CDATA XML Encoding
XML Encoding XML Server
XML Server XML DOM Advanced
XML DOM Advanced XML Don't
XML Don't XML Technologies
XML Technologies XML in Real Life
XML in Real Life XML Editors
XML Editors XML Summary
XML Summary
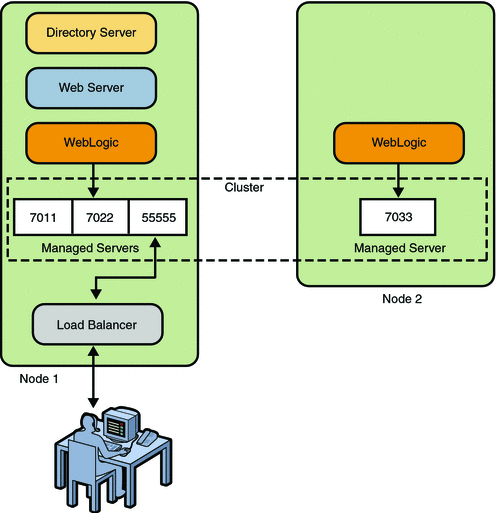
- a. Web Logic Introduction
- b. Weblogic Workshop
 File Types
File Types Applications and projects
Applications and projects Debugging application
Debugging application Managing build process
Managing build process Compiling
Compiling Source control systems
Source control systems Message logging
Message logging Developing web applications
Developing web applications
10. TOMCAT STRUTS
- a. Introduction
- b. Building Model Components
 JavaBeans and Scope
JavaBeans and Scope Action Form Beans
Action Form Beans System State Beans
System State Beans Business Logic Beans
Business Logic Beans- c. Building View Components
 Internationalization
Internationalization
 Forms and Form Bean Interactions
Forms and Form Bean Interactions Automatic Form Population
Automatic Form Population Automatic Form Validation
Automatic Form Validation The Struts Validator
The Struts Validator Page Composition With Tiles
Page Composition With Tiles Presentation Frameworks
Presentation Frameworks Direct Presentation Techniques
Direct Presentation Techniques Image Rendering Components
Image Rendering Components Rendering Text
Rendering Text
- d. Building Controller Components
 The ActionServlet
The ActionServlet ActionForm Classes
ActionForm Classes Action Classes
Action Classes  Exception Handler
Exception Handler Plugin Classes
Plugin Classes  The ActionMapping Implementation
The ActionMapping Implementation Writing ActionMappings
Writing ActionMappings  Using ActionMappings for Pages
Using ActionMappings for Pages Using Wildcards in ActionMappings
Using Wildcards in ActionMappings Using The Commons Logging Interface
Using The Commons Logging Interface- e. Configuring Applications
 The Configuration File
The Configuration File Configuring your application for modules
Configuring your application for modules The Web Application Deployment Descriptor
The Web Application Deployment Descriptor Add Framework Components To Your Application
Add Framework Components To Your Application Logging
Logging
