 Client/Server
Client/Server
 Peer-to-Peer
Peer-to-Peer LAN - Local Area Network
LAN - Local Area Network CAN - Campus Area Network
CAN - Campus Area Network MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
MAN - Metropolitan Area Network WAN - Wide Area Network
WAN - Wide Area Network How Do We Make Connections?
How Do We Make Connections? What is a Protocol?
What is a Protocol? Introduction to Addressing
Introduction to Addressing

About Diploma In Computer Network
Diploma in Computer Networking is open to anyone with the knowledge of hardware.This hands on course is our recommended cirriculam for those who want to upgrade from hardware to Networking. This course covers the full range of IBM and IBM-compatible systems. This is a preliminary course recommended for candidates wish to enter Network and System administration field.
Diploma In Computer Network Highlights
WHO WILL BENEFIT
COURSE CURRICULUM
What is a Network?
Network Media
 Wired Media - Twisted Pair, Coaxial, and Fiber Optic
Wired Media - Twisted Pair, Coaxial, and Fiber Optic
 What is the Plenum?
What is the Plenum? Common Connectors
Common Connectors Wiring Standards
Wiring Standards LAN Technology Types - Ethernet
LAN Technology Types - Ethernet Standard Ethernet
Standard Ethernet Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet 10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet Wiring Distriburtion
Wiring Distriburtion
Network Topologies
 What Does Topology Mean?
What Does Topology Mean?
 Bus,
Star,
Ring,
Mesh,
Hybrid,
Bus,
Star,
Ring,
Mesh,
Hybrid,
 WAN Technologies - Circuit and Pocket Switching
WAN Technologies - Circuit and Pocket Switching POTS, PSTN, T1/E1, and T3/E3
POTS, PSTN, T1/E1, and T3/E3 ISDN
ISDN SONET/OC-x
SONET/OC-x Frame Relay and ATM
Frame Relay and ATM MPLS - Multiprotocol Label Switching
MPLS - Multiprotocol Label Switching DSL
DSL Cable Modem, Satellite and Wireless
Cable Modem, Satellite and Wireless What is a VPN?
What is a VPN? What is a VLAN?
What is a VLAN?
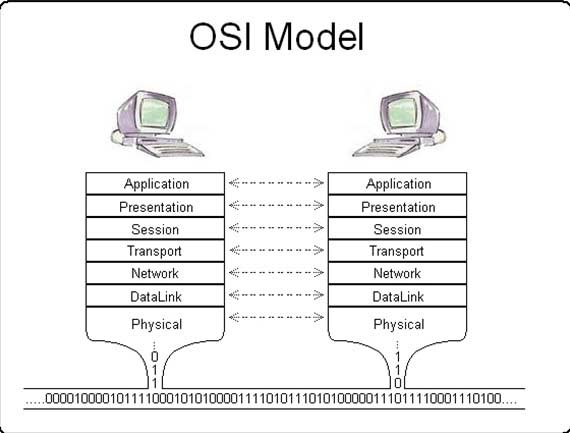
OSI Model
 Definition of a Protocol
Definition of a Protocol
 Standards of Communication
Standards of Communication What is the OSI Model?
What is the OSI Model? Defining OSI Model Layers
Defining OSI Model Layers How Data Travels Through OSI Model
How Data Travels Through OSI Model Networking Hardware in OSI Model
Networking Hardware in OSI Model
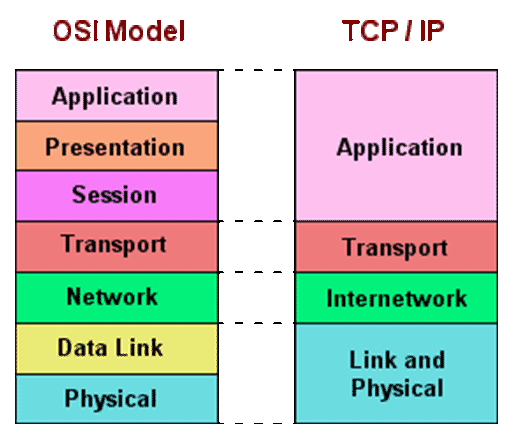
TCP/IP
 TCP/IP Protocol Suite
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
 What is TCP/IP (DARPA) Model?
What is TCP/IP (DARPA) Model?
 Transport Layer Protocols
Transport Layer Protocols
 Internet Layer Protocols
Internet Layer Protocols
 Types of TCP/IP Communication
Types of TCP/IP Communication
 Working with IP Addresses
Working with IP Addresses
 Planning an IP Addressing Scheme
Planning an IP Addressing Scheme
 Rules for IP Addressing
Rules for IP Addressing
 What is Classful IP Addressing?
What is Classful IP Addressing?
 Private vs. Public IP Addressing
Private vs. Public IP Addressing
 What is NAT?
What is NAT?
 How Computers Get IP Addresses
How Computers Get IP Addresses
 Working with Binary Numbers
Working with Binary Numbers
 Converting Binary to Decimal and Vice Versa
Converting Binary to Decimal and Vice Versa
 Binary IP Addresses
Binary IP Addresses
 Binary Subnet Masks
Binary Subnet Masks
 Internetworking - What is a Router?
Internetworking - What is a Router?
 What is a Default Gateway?
What is a Default Gateway?
 What is Subnetting?
What is Subnetting?
 Classful vs. Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR)
Classful vs. Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR)
 Subnetting with CIDR & VLSM
Subnetting with CIDR & VLSM
 CIDR Notation
CIDR Notation
TCP/IP Protocols
 FTP - File Transfer Protocol
FTP - File Transfer Protocol
 TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol
TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS NTP - Network Time Protocol
NTP - Network Time Protocol POP3 and IMAP4
POP3 and IMAP4 SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
 DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
 DNS - Domain Naming System
DNS - Domain Naming System Telnet and SSH
Telnet and SSH SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol
SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol SIP and RTP
SIP and RTP TLS - Transport Layer Security
TLS - Transport Layer Security
Network Devices
 Modem and NIC
Modem and NIC
 Repeater and Hub
Repeater and Hub
 Bridge and Switch
Bridge and Switch
 Router
Router
 Different Types of Switches
Different Types of Switches
 Advanced Switch Funcionality
Advanced Switch Funcionality
 Firewall and Proxy Server
Firewall and Proxy Server
 Wireless Access Point
Wireless Access Point
 Basic DHCP Server and DNS Server
Basic DHCP Server and DNS Server
 CSU/DSU
CSU/DSU
 Media Converters
Media Converters
 Load Balancer and Bandwidth Shaper
Load Balancer and Bandwidth Shaper
Routing
 Understanding Routing Tables
Understanding Routing Tables
 Adding and Deleting Routes
Adding and Deleting Routes
 Static vs. Dynamic Routing
Static vs. Dynamic Routing
 Routing Protocols
Routing Protocols
 Distance Vector Protocols: RIP, RIPv2, and BGP
Distance Vector Protocols: RIP, RIPv2, and BGP
 Link State Protocols: OSPF and IS-IS
Link State Protocols: OSPF and IS-IS
 Hybrid Routing Protocol: EIGRP
Hybrid Routing Protocol: EIGRP
 What is Convergence?
What is Convergence?
 IGP vs. EGP
IGP vs. EGP
Wireless Networking
 Benefits of Wireless Networking
Benefits of Wireless Networking
 Components of a Wireless Access Point
Components of a Wireless Access Point
 Where to Place a WAP
Where to Place a WAP
 Wireless Networking Standards
Wireless Networking Standards
 RF Channels
RF Channels
 How to Secure a Wireless Network
How to Secure a Wireless Network
 WEP - Wired Equivalency Privacy
WEP - Wired Equivalency Privacy
 WPA - Wi-Fi Protected Access
WPA - Wi-Fi Protected Access
 802.1x
802.1x
 Setting Up a Wireless Access Point
Setting Up a Wireless Access Point
Networking Command Line Tools
 ipconfig/ifconfig/arp Utilities Overview
ipconfig/ifconfig/arp Utilities Overview
 ping/arp ping Utilities Overview
ping/arp ping Utilities Overview tracert/traceroute Utilities Overview
tracert/traceroute Utilities Overview mtr Utility Overview
mtr Utility Overview netstat/nbstat/route Utilities Overview
netstat/nbstat/route Utilities Overview nslookup/dig/host Utilities Overview
nslookup/dig/host Utilities Overview
 ipconfig Command
ipconfig Command
 arp Command
arp Command ping Command
ping Command
 tracert Command
tracert Command netstat Command
netstat Command
 nslookup Command
nslookup Command

Network Performance Optimization
 Reasons for Network Performance Optimization
Reasons for Network Performance Optimization
 Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) Traffic Shaping
Traffic Shaping Load Balancing
Load Balancing Fault Tolerance
Fault Tolerance RAID 0 - Disk Striping
RAID 0 - Disk Striping RAID 1 - Disk Mirroring and Duplexing
RAID 1 - Disk Mirroring and Duplexing RAID 5 - Disk Striping with Parity
RAID 5 - Disk Striping with Parity Other Popular Forms of RAID
Other Popular Forms of RAID Caching Engines
Caching Engines
Network Tools
 Cable Strippers
Cable Strippers
 Snips and Crimpers
Snips and Crimpers Punch Down Tool
Punch Down Tool Cable Testers and Certifiers
Cable Testers and Certifiers Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) and Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR)
Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) and Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) Toner Probe
Toner Probe Voltage Event Recorder
Voltage Event Recorder Multimeter
Multimeter Protocol Analyzer, Temperature Monitor, and Butt Set
Protocol Analyzer, Temperature Monitor, and Butt Set

Network Monitoring
 Packet Sniffers
Packet Sniffers
 Port Scanners
Port Scanners Intrusion Detection Software (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Software (IPS)
Intrusion Detection Software (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Software (IPS) System, Event, and History Logs
System, Event, and History Logs
Documentation
 Why is Documentation so Important?
Why is Documentation so Important?
 What Should I Document?
What Should I Document? Wiring Schematics
Wiring Schematics Physical and Logical Network Diagrams
Physical and Logical Network Diagrams Baseline
Baseline Network Policies
Network Policies Network Procedures
Network Procedures Network Configuration
Network Configuration Regulations
Regulations
Troubleshooting
 The Process of Troubleshooting - Gather Information
The Process of Troubleshooting - Gather Information
 Who is Affected?
Who is Affected? What's Changed?
What's Changed? Why is This Happening?
Why is This Happening? Can I Handle It?
Can I Handle It? Process of Finding a Solution
Process of Finding a Solution Physical Issues
Physical Issues Logical Issues
Logical Issues Issues to Escalate
Issues to Escalate Wireless Issues
Wireless Issues CMOS Setting
CMOS Setting Operating System Troubleshooting
Operating System Troubleshooting Hardware Troubleshooting
Hardware Troubleshooting
Network Security
 Firewalls
Firewalls
 Other Security Devices
Other Security Devices Network Access Security
Network Access Security Filtering
Filtering Tunneling and Encryption
Tunneling and Encryption User Authentication
User Authentication Device Security
Device Security Common Security Threats
Common Security Threats

