Diploma in System Programming Details
DSP is a fundamental course recommended for all the students whose goal is to understand the concept of Programming language and its implementation in the real time world. We Cover C, C++ and Linux Operating system to give a firm foundation for a career as systems programmer.
System programming consists of the design and writing of computer programs that permit the computer hardware to connect to the programmer and the user, which allow the application software to be run effectively on the computer system. Typical system programs included an Operating System and firmware, compiler programming tools, assemblers, I / O routines, interpreters, schedulers, loaders, linkers as well as computer programming language runtime libraries.
System programming is a vital and important foundation for the development of every computer application and it is evolving always to accommodate computer hardware changes. The programmers must therefore be aware of the hardware they are supposed to use to operate. This kind of programming needs some hardware knowledge and depends on the machine.
The development of computer system software that manages and controls computer operations is the result of system programming. The low-level codes are very close to the hardware level and deal with registries and the allocation of memories. System programs or software co-ordinate the transfer of data between different components and processes the compilation, linking, starting and stopping of programs, reading files and typing in files.
Diploma in System Programming Highlights
[A]. C Programming
Course outline
 Introduction to compiling and software development
Introduction to compiling and software development  Basic scalar data types and their operators
Basic scalar data types and their operators  Flow control
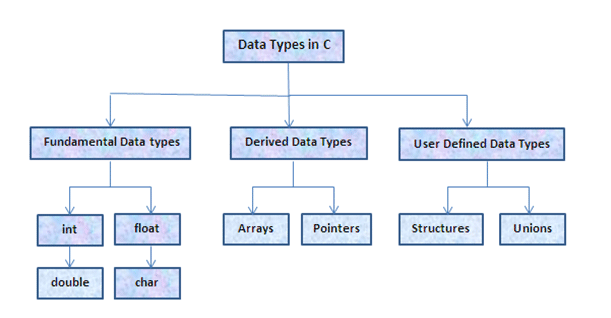
Flow control  Complex data types: arrays, structures and pointers
Complex data types: arrays, structures and pointers  Structuring the code: functions and modules
Structuring the code: functions and modules  Preprocessing source code
Preprocessing source code
Chapters
 Absolute basics
Absolute basics  Languages: natural and artificial
Languages: natural and artificial  Machine languages
Machine languages  High-level programming languages
High-level programming languages  Obtaining the machine code: compilation process
Obtaining the machine code: compilation process  Recommended readings
Recommended readings  Your first program
Your first program  Variable – why?
Variable – why?  Integer values in real life and in “C”, integer literals
Integer values in real life and in “C”, integer literals
 Floating point values in real life and in “C”, float literals
Floating point values in real life and in “C”, float literals  Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic operators  Priority and binding
Priority and binding  Post- and pre -incrementation and -decrementation
Post- and pre -incrementation and -decrementation  Operators of type op=
Operators of type op=  Char type and ASCII code, char literals
Char type and ASCII code, char literals  Equivalence of int and char data
Equivalence of int and char data  Comparison operators
Comparison operators  Conditional execution and if keyword
Conditional execution and if keyword
 printf() and scanf() functions: absolute basics
printf() and scanf() functions: absolute basics
 Flow control
Flow control
 Conditional execution continued: the “else” branch
Conditional execution continued: the “else” branch
 More integer and float types
More integer and float types
 Conversions – why?
Conversions – why?
 Typecast and its operators
Typecast and its operators
 Loops – while, do and for
Loops – while, do and for
 Controlling the loop execution – break and continue
Controlling the loop execution – break and continue
 Logical and bitwise operators
Logical and bitwise operators
 Switch: different faces of ‘if’
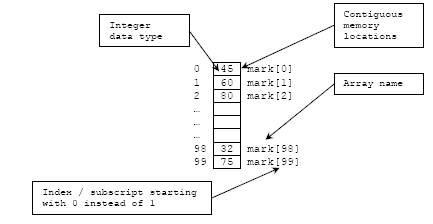
Switch: different faces of ‘if’  Arrays (vectors) – why do you need them?
Arrays (vectors) – why do you need them?  Sorting in real life and in a computer memory
Sorting in real life and in a computer memory  Initiators: a simple way to set an array
Initiators: a simple way to set an array  Pointers: another kind of data in “C”
Pointers: another kind of data in “C”  An address, a reference, a dereference and the sizeof operator
An address, a reference, a dereference and the sizeof operator  Simple pointer and pointer to nothing (NULL) & operator
Simple pointer and pointer to nothing (NULL) & operator  Pointers arithmetic
Pointers arithmetic  Pointers vs. arrays: different forms of the same phenomenon
Pointers vs. arrays: different forms of the same phenomenon  Using strings: basics
Using strings: basics  Basic functions dedicated to string manipulation
Basic functions dedicated to string manipulation
 Memory management and structures
Memory management and structures  The meaning of array indexing
The meaning of array indexing  The usage of pointers: perils and disadvantages
The usage of pointers: perils and disadvantages Void type
Void type  Arrays of arrays and multidimensional arrays
Arrays of arrays and multidimensional arrays  Memory allocation and deallocation: malloc() and free() functions
Memory allocation and deallocation: malloc() and free() functions  Arrays of pointers vs. multidimensional arrays
Arrays of pointers vs. multidimensional arrays Structures – why?
Structures – why?  Declaring, using and initializing structures
Declaring, using and initializing structures Pointers to structures and arrays of structures
Pointers to structures and arrays of structures  Basics of recursive data collections
Basics of recursive data collections
 Functions – why?
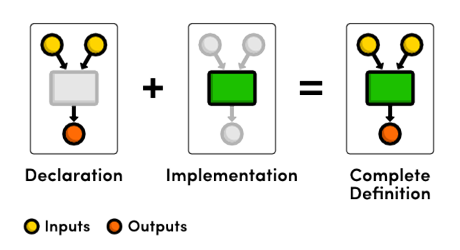
Functions – why?  How to declare, define and invoke a function
How to declare, define and invoke a function Variables' scope, local variables and function parameters
Variables' scope, local variables and function parameters  Pointers, arrays and structures as function parameters
Pointers, arrays and structures as function parameters  Function result and return statement
Function result and return statement
 Void as a parameter, pointer and result
Void as a parameter, pointer and result
 Parameterzing the main function
Parameterzing the main function
 External function and the extern declarator
External function and the extern declarator
 Header files and their role
Header files and their role
 Files vs. streams: where does the difference lie?
Files vs. streams: where does the difference lie? Header files needed for stream operations
Header files needed for stream operations
 Opening and closing a stream, open modes, errno variable
Opening and closing a stream, open modes, errno variable Reading and writing to/from a stream
Reading and writing to/from a stream  Predefined streams: stdin, stdout and stderr
Predefined streams: stdin, stdout and stderr  Stream manipulation: fgetc(), fputc(), fgets() and fputs() functions
Stream manipulation: fgetc(), fputc(), fgets() and fputs() functions  Raw input/output: fread() and fwrite() functions
Raw input/output: fread() and fwrite() functions  Preprocessor and complex declarations
Preprocessor and complex declarations  Preprocessor – why?
Preprocessor – why?  #include: how to make use of a header file
#include: how to make use of a header file
 #define: simple and parameterized macros
#define: simple and parameterized macros  #undef directive
#undef directive Predefined preprocessor symbols
Predefined preprocessor symbols Macro operators: # and ##
Macro operators: # and ##  Conditional compilation: #if and #ifdef directives
Conditional compilation: #if and #ifdef directives  Avoiding multiple compilations of the same header files
Avoiding multiple compilations of the same header files  Scopes of declarations, storage classes
Scopes of declarations, storage classes  User defined types-why?
User defined types-why?  Pointers to functions
Analyzing and creating complex declarations
Pointers to functions
Analyzing and creating complex declarations
[B]. C++ Programming Language
Description
Objective
Prerequisite
 What is C++? , Why C++?
What is C++? , Why C++?  C and C++
C and C++  Exception Handling
Exception Handling  Object Oriented Programming
Object Oriented Programming  Standard Template Library
Standard Template Library
 Types
Types  Booleans
Booleans  Integer Types
Integer Types  Floating-Point Types
Floating-Point Types Sizes
Sizes  Void
Void  Enumerations
Enumerations  Declarations
Declarations


 Pointers
Pointers  Arrays
Arrays  Pointers into Arrays
Pointers into Arrays  Constants
Constants  References
References  Pointers to void
Pointers to void  Structures
Structures
 A Deck Calculator
A Deck Calculator  Operator Summary
Operator Summary  Statement Summary
Statement Summary  Comments and Indentation
Comments and Indentation
 Function Declarations
Function Declarations  Argument Passing
Argument Passing  Value Return
Value Return  Overloaded Function Names
Overloaded Function Names  Default Arguments
Default Arguments  Pointer to Function
Pointer to Function  Macros
Macros
 Namespaces
Namespaces
 Exceptions
Exceptions
 Separate Compilation
Separate Compilation Linkage
Linkage  Using Header Files
Using Header Files  Programs
Programs
 Classes
Classes  Access Control
Access Control  Constructors
Constructors  Member functions
Member functions Static members
Static members  Destructors
Destructors Memory allocation
Memory allocation  Member initialization
Member initialization
 Introduction
Introduction  Operator Functions
Operator Functions A Complete Number Type
A Complete Number Type  Conversion Operators
Conversion Operators  Friends
Friends  Large Objects
Large Objects  Essential Operators
Essential Operators  Subscripting
Subscripting  Functions Calls
Functions Calls  Dereferencing
Dereferencing  Increment and Decrement
Increment and Decrement  A String Class
A String Class
 Introduction
Introduction
 Derived Classes
Derived Classes
 Abstract Classes
Abstract Classes
 Design of Class Hierarchies
Design of Class Hierarchies
 Class Hierarchies and Abstract Classes
Class Hierarchies and Abstract Classes
[C]. Linux Basic commands
| Linux Basic commands |
 History,features of unix, difference between Unix and Linux History,features of unix, difference between Unix and Linux |
| Unix System Architecture |
 Kernel,Shells and GUI and File system Kernel,Shells and GUI and File system |
 Application Program,Shell prompt Application Program,Shell prompt |
| Login process |
 TTY terminal,Graphical terminal, Changing password TTY terminal,Graphical terminal, Changing password |
| Unix Command Format |
 General rules for a unix command, types of commands General rules for a unix command, types of commands |
| General purpose Commands |
 echo,printf,tput,cal,date,tty,Uname,Who,Who am I,bc, pr echo,printf,tput,cal,date,tty,Uname,Who,Who am I,bc, pr |
| Unix File System |
 Unix File System Architecture,Types of files Unix File System Architecture,Types of files
|
| Directory Related Commands |
 pwd,cd,mkdir,rdir,creation of sub directory pwd,cd,mkdir,rdir,creation of sub directory |
| File Related Commands |
 cat,cp,mv,rm,touch,ls, commands to display the conents of file. cat,cp,mv,rm,touch,ls, commands to display the conents of file. |
 comparing files,file permission notation,File access permission comparing files,file permission notation,File access permission |
 chaning file permissions. chaning file permissions. |
| I/O Redirecton |
 Pipe and Pipeline,Filter(sort,cut,paste,uniq,tr,wc,cat,grep) Pipe and Pipeline,Filter(sort,cut,paste,uniq,tr,wc,cat,grep) |
| The Stream Editor(sed) |
 sed commands sed commands |
| Unix system calls |
 open,close,unlink,lseek,fork,wait open,close,unlink,lseek,fork,wait |
| Compressign and Decompressing File, Communicaton |
| Shell programming |
 Vi editor, execute shell script Vi editor, execute shell script |
 control statements, looping statements,programs on shell control statements, looping statements,programs on shell |

