
About Cloud Computing Training
Cloud computing offers your business many benefits. It allows you to set up what is essentially a virtual office to give you the flexibility of connecting to your business anywhere, any time. With the growing number of web-enabled devices used in today's business environment (e.g. smartphones, tablets), access to your data is even easier. There are many benefits to moving your business to the cloud
CLOUD COMPUTING TRAINING HIGHLIGHTS
Course Duration
1 month
8 WeekendsLearners
50000
Delivery Mode
Class Room Training
Apply Online
CLOUD COMPUTING COURSE OUTCOME
WHO WILL BENEFIT
CLOUD COMPUTING COURSE CURRICULUM
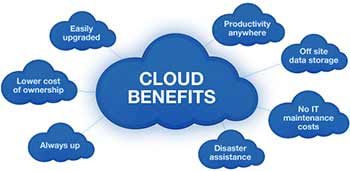
Reduced IT costs
Moving to cloud computing may reduce the cost of managing and maintaining your IT systems. Rather than purchasing expensive systems and equipment for your business, you can reduce your costs by using the resources of your cloud computing service provider. You may be able to reduce your operating costs because:
 the cost of system upgrades, new hardware and software may be included in your contract
the cost of system upgrades, new hardware and software may be included in your contract you no longer need to pay wages for expert staff
you no longer need to pay wages for expert staff your energy consumption costs may be reduced
your energy consumption costs may be reduced  there are fewer time delays.
there are fewer time delays.
Scalability
Your business can scale up or scale down your operation and storage needs quickly to suit your situation, allowing flexibility as your needs change. Rather than purchasing and installing expensive upgrades yourself, your cloud computer service provider can handle this for you. Using the cloud frees up your time so you can get on with running your business.
Business continuity
Protecting your data and systems is an important part of business continuity planning. Whether you experience a natural disaster, power failure or other crisis, having your data stored in the cloud ensures it is backed up and protected in a secure and safe location. Being able to access your data again quickly allows you to conduct business as usual, minimising any downtime and loss of productivity.
Collaboration efficiency
Collaboration in a cloud environment gives your business the ability to communicate and share more easily outside of the traditional methods. If you are working on a project across different locations, you could use cloud computing to give employees, contractors and third parties access to the same files. You could also choose a cloud computing model that makes it easy for you to share your records with your advisers (e.g. a quick and secure way to share accounting records with your accountant or financial adviser).
Flexibility of work practices
Cloud computing allows employees to be more flexible in their work practices. For example, you have the ability to access data from home, on holiday, or via the commute to and from work (providing you have an internet connection). If you need access to your data while you are off-site, you can connect to your virtual office, quickly and easily.
Access to automatic updates
Access to automatic updates for your IT requirements may be included in your service fee. Depending on your cloud computing service provider, your system will regularly be updated with the latest technology. This could include up-to-date versions of software, as well as upgrades to servers and computer processing power.
Cloud Computing Course Contents
| 1.Introduction to Cloud Computing |
 Defining cloud computing Defining cloud computing |
 Components of a computing cloud Components of a computing cloud |
 Differentiating types of clouds: public, private, hybrid Differentiating types of clouds: public, private, hybrid |
 Delivering services from the cloud Delivering services from the cloud |
 Categorizing service types Categorizing service types |
 Comparing vendor cloud products: Amazon, Google, Microsoft and others Comparing vendor cloud products: Amazon, Google, Microsoft and others |
| 2.Adopting the Cloud |
 Key drivers of cloud computing solutions Key drivers of cloud computing solutions |
 Instantaneous provisioning of computing resources Instantaneous provisioning of computing resources |
 Handling varied loads with elasticity and seamless scalability Handling varied loads with elasticity and seamless scalability |
 Tapping into an infinite storage capacity Tapping into an infinite storage capacity |
 Cost-effective pay-as-you-use billing models Cost-effective pay-as-you-use billing models |
 Evaluating barriers to cloud computing Evaluating barriers to cloud computing |
 Handling sensitive data Handling sensitive data |
 Aspects of cloud security Aspects of cloud security |
 Assessing governance solutions Assessing governance solutions |
| 3.Exploiting Software as a Service (SaaS) |
 Characterizing SaaS Characterizing SaaS |
 Minimizing the need for local hardware and software Minimizing the need for local hardware and software |
 Streamlining administration with centralized installation and updates Streamlining administration with centralized installation and updates |
 Optimizing cost and performance with the ability to scale on demand Optimizing cost and performance with the ability to scale on demand |
 Comparing service scenarios Comparing service scenarios |
 Improving collaboration with business productivity tools Improving collaboration with business productivity tools |
 Simplifying business process creation by integrating existing components Simplifying business process creation by integrating existing components |
 Inspecting SaaS technologies Inspecting SaaS technologies |
 Deploying Web applications Deploying Web applications |
 Implementing Web services: SOAP, REST Implementing Web services: SOAP, REST |
 Choosing a development platform Choosing a development platform |
| 4.Delivering Platform as a Service (PaaS) |
 Exploring the technical foundation for PaaS Exploring the technical foundation for PaaS |
 Specifying the components of PaaS Specifying the components of PaaS |
 Analyzing vendor PaaS provisions Analyzing vendor PaaS provisions |
 Selecting an appropriate implementation Selecting an appropriate implementation |
 Building services with solution stacks Building services with solution stacks |
 Evaluating the architecture of vendor specific platforms Evaluating the architecture of vendor specific platforms |
 Becoming familiar with service platform tools Becoming familiar with service platform tools |
 Leveraging the power of scalable middleware Leveraging the power of scalable middleware |
 Managing cloud storage Managing cloud storage |
 Controlling unstructured data in the cloud Controlling unstructured data in the cloud |
 Deploying relational databases in the cloud Deploying relational databases in the cloud |
 Improving data availability Improving data availability |
 Employing support services Employing support services |
 Testing in the cloud Testing in the cloud |
 Monitoring cloud-based services Monitoring cloud-based services |
 Analyzing portability across platforms Analyzing portability across platforms |
| 5.Deploying Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
 Enabling technologies Enabling technologies |
 Scalable server clusters Scalable server clusters |
 Achieving transparency with platform virtualization Achieving transparency with platform virtualization |
 Elastic storage devices Elastic storage devices |
 Accessing IaaS Accessing IaaS |
 Provisioning servers on demand Provisioning servers on demand |
 Handling dynamic and static IP addresses Handling dynamic and static IP addresses |
 Tools and support for management and monitoring Tools and support for management and monitoring |
| 6.Building a Business Case |
 Calculating the financial implications Calculating the financial implications |
 Analyzing current and future computing requirements Analyzing current and future computing requirements |
 Comparing in-house facilities to the cloud Comparing in-house facilities to the cloud |
 Estimating economic factors downstream Estimating economic factors downstream |
 Preserving business continuity Preserving business continuity |
 Selecting appropriate service-level agreements Selecting appropriate service-level agreements |
 Safeguarding access to assets in the cloud Safeguarding access to assets in the cloud |
 Security, availability and disaster recovery strategies Security, availability and disaster recovery strategies |
| 7.Migrating to the Cloud |
 Technical considerations Technical considerations |
 Rearchitecting applications for the cloud Rearchitecting applications for the cloud |
 Integrating the cloud with existing applications Integrating the cloud with existing applications |
 Avoiding vendor lock-in Avoiding vendor lock-in |
 Planning the migration Planning the migration |
 Incremental vs Incremental vs |
 one-step solution one-step solution |
 Selecting a vendor Selecting a vendor |
 Establishing staff skill requirements Establishing staff skill requirements |
